Conquering the Project Management Mountain: A
Visual Guide for PMP Aspirants
Welcome, PMP aspirants! As you embark on your
project management journey, navigating the vast landscape of methodologies can
feel overwhelming. But fear not! This blog post is your compass, guiding you
through the key concepts with clear explanations and helpful visuals.
Understanding the Big Picture: Project
Methodologies and life cycles
Imagine a project as a delicious cake,
methodologies are like the recipes, providing a structured framework for baking
the cake (think Waterfall, Agile, etc.).
- Agile: Embraces flexibility
and iteration, adapting to changing requirements through short sprints.
It's like baking your cake in batches, testing and refining each layer
before moving on.
- Hybrid: Blends elements of
both Waterfall and Agile, catering to projects with specific needs. This
is like customizing your cake recipe with unique ingredients and
techniques.
A Sequential Approach to Project Management
The Waterfall Methodology is one of the
earliest and most traditional approaches to project management. It follows a
linear and sequential process, where each phase must be completed before moving
on to the next. This method is particularly well-suited for projects with
well-defined and stable requirements, where changes are expected to be minimal
once the project begins.
Let's delve into the key stages and
characteristics of the Waterfall Methodology:
1. Initiation:
- Definition of Project Scope:Clearly defining the project's objectives, deliverables, constraints, and assumptions.
- Stakeholder Identification:Identifying and engaging with stakeholders to understand their expectations and requirements.
2. Planning:
- Detailed Project Plan:Creating a comprehensive project plan that outlines tasks, timelines, resource requirements, and dependencies.
- Risk Analysis:Identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies.
3. Execution:
- Building and Development:Actual implementation of the project based on the defined requirements and project plan.
- Quality Assurance:Ensuring that the project's deliverables meet the specified quality standards.
4. Monitoring and Controlling:
- Progress Tracking:Regularly monitoring project progress against the established plan.
- Change Control:Managing changes carefully to avoid scope creep and maintain project integrity.
5. Closing:
- Client Approval:Obtaining client or stakeholder approval for project deliverables.
- Final Documentation:Completing all necessary documentation and closing out the project.
Advantages of the Waterfall
Methodology:
- Clear Structure:Well-defined stages and deliverables provide a clear roadmap for the project.
- Client Involvement:Client involvement mainly occurs during the initial stages, ensuring their requirements are accurately captured.
- Easier to Manage:Due to its sequential nature, the Waterfall Methodology is often easier to manage and document.
Challenges of the Waterfall
Methodology:
- Rigidity:Limited flexibility can be a challenge when dealing with evolving or unclear requirements.
- Late Changes:Changes are challenging to incorporate once the project is in the execution phase.
- Client Feedback:Limited client interaction during the development phase can result in misalignments with client expectations.
The Waterfall Methodology provides a
structured and systematic approach to project management. While it may not be
suitable for every project, particularly those with dynamic or evolving
requirements, it remains a valuable option for projects where a well-defined
plan is essential from the outset. As you explore project management
methodologies, understanding the intricacies of the Waterfall Methodology will
broaden your knowledge and help you make informed decisions in your project
management journey.
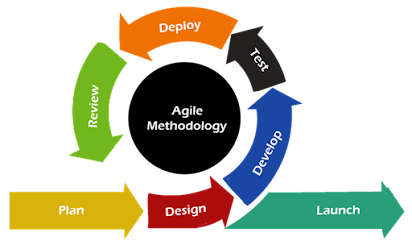
2. Agile Methodology :-
In the dynamic landscape of project management, the Agile methodology has emerged as a beacon of adaptability, collaboration, and efficiency. Agile is more than just a methodology; it's a mindset that emphasizes iterative and incremental progress. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the core principles, practices, and benefits of Agile, with a specific focus on its iterative and incremental nature.
Understanding Agile: A Paradigm
Shift
1. Agile Principles:
- Individuals and
interactions over processes and tools.
- Working solutions over
comprehensive documentation.
- Customer collaboration over
contract negotiation.
- Responding to change over
following a plan.
- Iterations (Sprints): Agile
projects are divided into fixed-length iterations called sprints,
typically lasting 2-4 weeks. Each sprint results in a potentially
shippable product increment.
- Increments: The project
progresses through a series of increments, with each increment building
upon the previous one. This iterative approach allows for continuous
improvement and flexibility.
- Roles: Scrum defines
specific roles, including a Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development
Team.
- Artifacts: Key artifacts
include the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment.
- Ceremonies: Scrum
ceremonies, such as Sprint Planning, Daily Standups, Sprint Review, and
Sprint Retrospective, ensure regular communication and feedback.
2. Kanban:
- Visualization: Kanban uses
visual boards to represent work items and their status, providing a
real-time overview of the project.
- Work in Progress (WIP)
Limits: Limits on WIP prevent overloading the team, promoting a steady and
controlled workflow.
- Continuous Delivery: Kanban
emphasizes continuous delivery, allowing teams to release increments as
soon as they are completed.
1. Adaptability:Agile welcomes changes in requirements, even late in the development process. This flexibility ensures that the project remains aligned with evolving needs.
2. Collaboration:Cross-functional teams collaborate closely, fostering a culture of communication, shared responsibility, and collective problem-solving.
3. Continuous Feedback:Regular feedback loops, including sprint reviews and retrospectives, enable teams to assess their performance and make improvements.
Benefits of Agile Methodology
2. Customer Satisfaction:Regular deliveries and feedback loops ensure that the final product aligns closely with customer expectations.
3. Reduced Risk:Incremental progress minimizes the impact of potential issues, leading to lower project risk.
Embracing the Agile Mindset for Success
In conclusion, Agile methodology stands as a
testament to the power of iterative and incremental development. By
prioritizing adaptability, collaboration, and continuous improvement, Agile
provides a robust framework for achieving project success in an ever-evolving
landscape. Whether you're a project manager, a team member, or a stakeholder,
embracing the Agile mindset can pave the way for efficient, customer-focused,
and ultimately successful projects.
3. Hybrid Methodology:-
I. Understanding the Hybrid
Methodology
1. Integration of Waterfall and Agile:
- Waterfall Elements:
Sequential stages, detailed planning, and well-defined requirements.
- Agile Elements: Iterative
development, flexibility to changes, and continuous feedback.
2. Tailored Approach:
- Adapts to the unique needs
of each project.
- Allows for a phased
approach with milestones.
- Enables quick responses to
unforeseen challenges.
2. Sequential and Iterative Integration:Utilizes sequential stages for planning and certain phases,Incorporates iterative cycles for development and testing.
3. Emphasis on Communication:Encourages continuous collaboration between teams.Prioritizes stakeholder engagement throughout the project.
III. Benefits of Adopting a
Hybrid Approach
- Maximizes efficiency and
minimizes risks.
2. Risk Mitigation:Identifies and addresses potential issues early in the project.
- Integrates feedback loops
for continuous improvement.
3. Enhanced Stakeholder Satisfaction:Offers a structured approach for planning and reporting.
- Embraces changes based on
stakeholder feedback.
- Evaluate project
characteristics, complexity, and scope.
- Determine the suitability
of a Hybrid approach.
2. Tailoring Processes:
- Customize processes based
on the chosen elements.
- Define the sequential and
iterative components.
3. Project Management Tools:
- Utilize tools that support
both Waterfall and Agile practices.
- Enhance collaboration and
communication.
- Requires careful balancing
of sequential and iterative elements.
- Continuous monitoring and
adjustment are essential.
2. Team Training:
- Ensure teams are familiar
with both Waterfall and Agile practices.
- Provide training to bridge any knowledge gaps.
The Hybrid Methodology offers organizations
the flexibility to tailor their approach, incorporating the strengths of both
Waterfall and Agile methodologies. By understanding its principles, benefits,
and implementation considerations, project managers can strategically leverage
this adaptable framework to navigate the complexities of various projects. As
the project management landscape continues to evolve, the Hybrid Methodology
stands out as a powerful tool for achieving successful project outcomes.
Assessment of Project Needs,
Complexity, and Magnitude
We've explored the diverse landscapes of Waterfall,
Agile, and Hybrid methodologies, unveiling their strengths and weaknesses. So,
the burning question remains: which path should you choose?
The answer, like a true adventurer's spirit, lies
within you. Consider your project's unique terrain – its complexity, your
team's dynamics, and your organization's culture.
- For well-defined journeys
with minimal detours, Waterfall's structured path offers a clear
roadmap. Embrace its meticulous planning and defined phases if
predictability is your guiding star.
- If your landscape shimmers
with uncertainty, Agile's flexible ascent will be your best
friend. Welcome change, adapt to evolving goals, and
conquer the unknown with iterative sprints.
- But remember, heroes often
forge their own paths. The Hybrid methodology allows you to blend
elements of both, crafting a custom ascent that perfectly fits your
project's unique challenges.